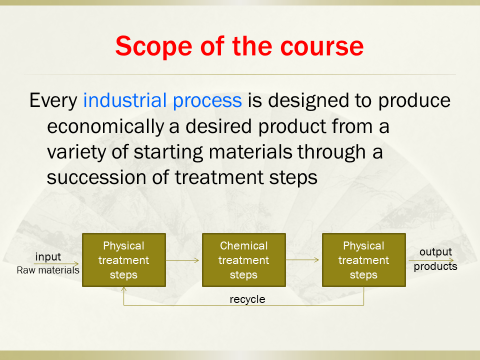
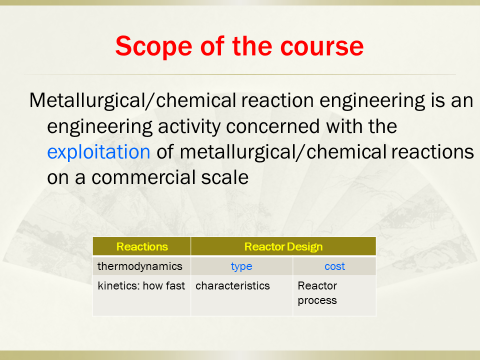
《MetallurgicalReaction Engineering》苏州大学面向冶金工程和金属材料工程专业开设的一门全英文课程。The core elements of the course include (i) thermodynamics, (ii)kinetics, (iii) transport processes, (iv) types of reactors, (v) mode ofoperation and contacting, (vi) modeling and optimization, and (vii) control.
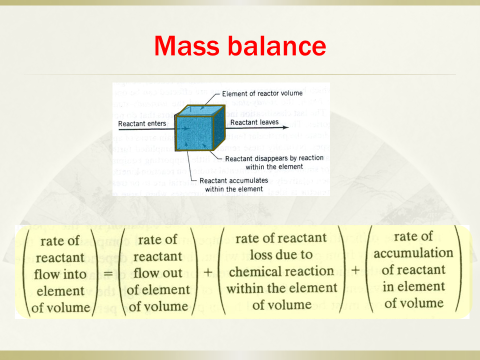
Thermodynamics deals with the feasibility of reaction;kinetics provides information about the rate at which a reactant is consumed;transport processes usually use continuum equations for mass, heat and momentumtransfer; types of reactors include ideal reactors and actual reactors; mode ofoperation and contacting are classified as batch, semi-batch and continuous;modeling, optimization and control permit prediction of the conversion,selectivity (for systems with multiple reactions), of patterns and hot spots orregions of high temperature. Thermodynamics, kinetics and transport theory arethe fundamentals for designing and operating reactors to achieve the highestefficiency.
In order to inspire creativity, the lessons will bestructured in such a way as to guide the students to apply fundamentals, fullyexplicated in advance, to reactor design and control.
The course is divided into ten chapters.
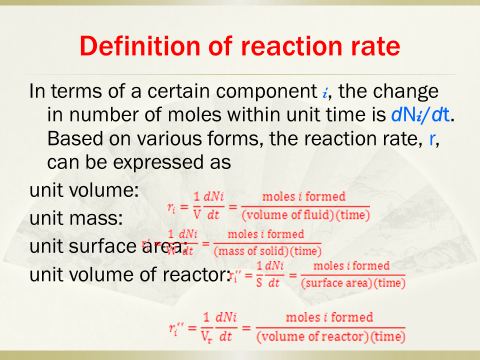
1. Introductionto the course, definition of reaction rate, variables affecting reaction rate
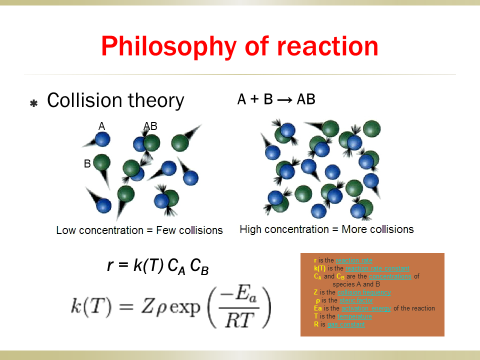
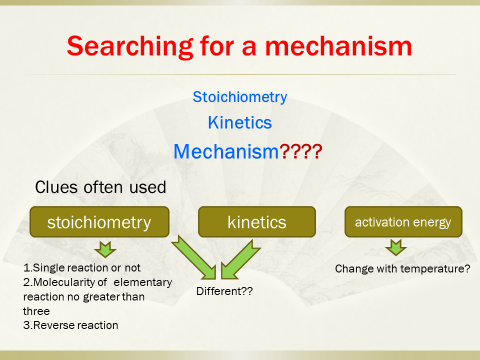
2. Searchingfor a reaction mechanism, concentration-dependent term andtemperature-dependent term
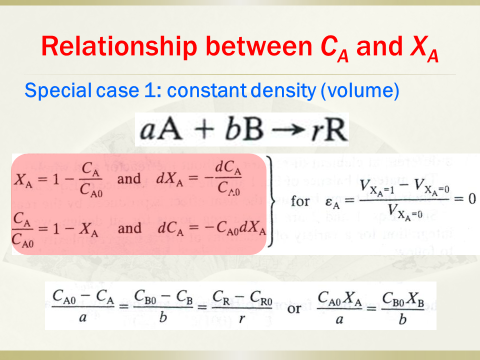
3. Introductionof conversion, rate expression in batch reactors at conditions of constantvolume and changing volume
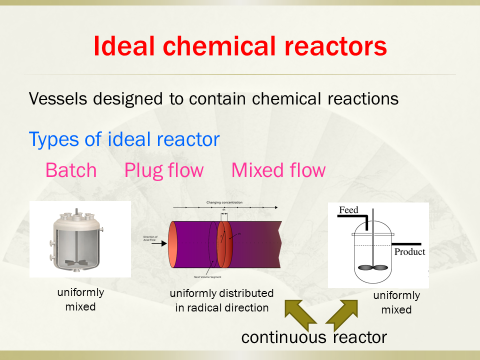
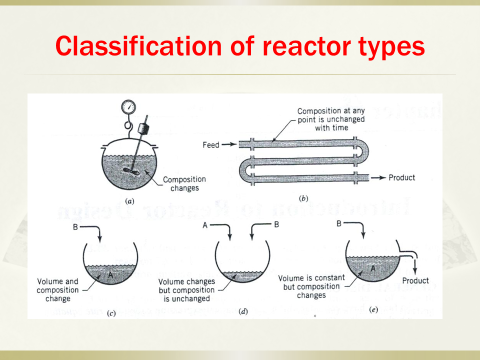
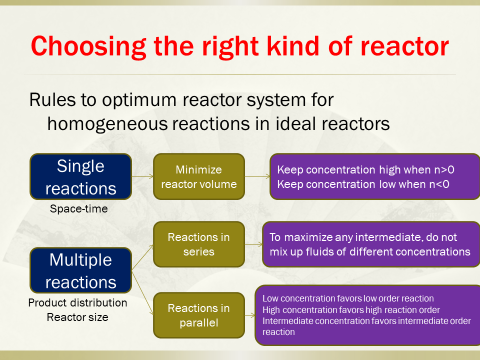
4. Analyzingperformance of ideal reactors, designing reactors appropriate to certainreaction types
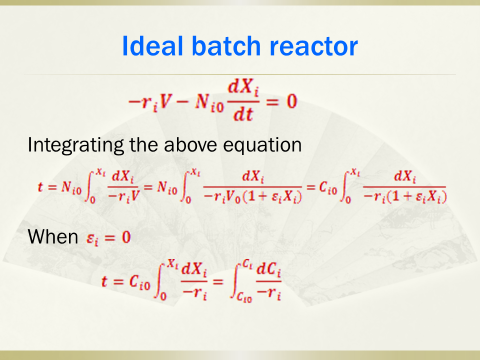
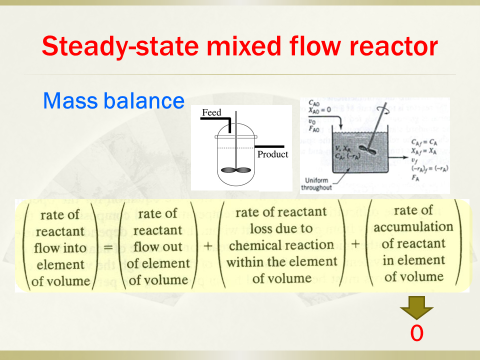
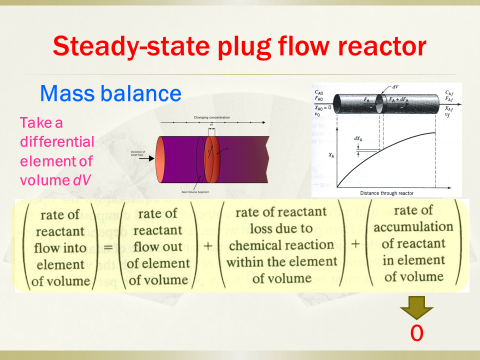
5. Analyticalsolution for various orders of reactions in batch reactors, plug flow reactorsand mixed flow reactors
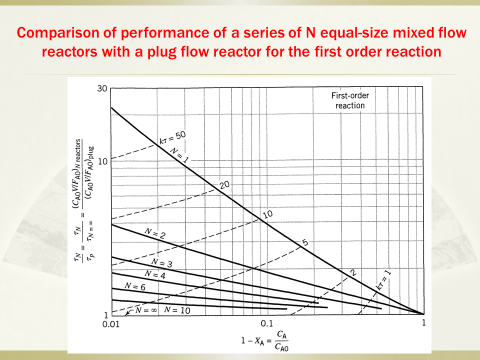
6. Designingthe most suitable reactor combination for single reactions
7. Designingthe most suitable reactor combination for parallel reactions
8. Designingthe most suitable reactor combination for multiple reactions of variousreaction orders
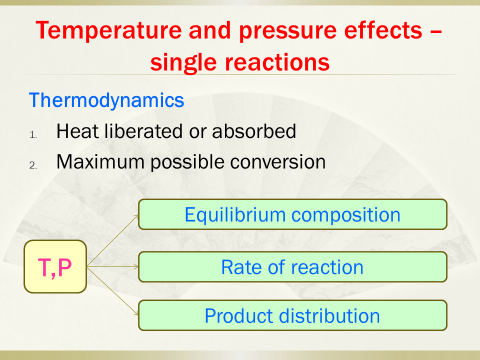
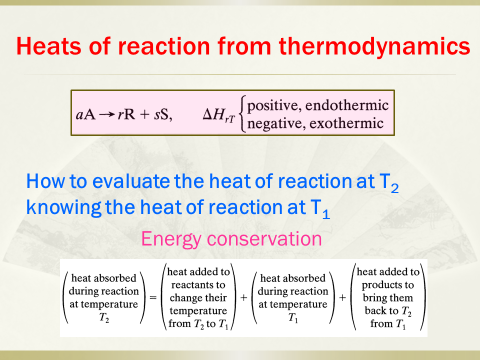
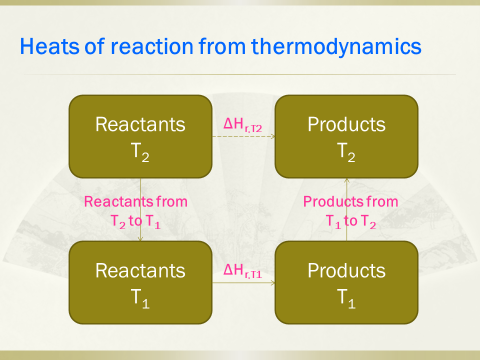
9. Thermodynamicsof reactions, heat effect, graphical design procedure and optimal temperatureprogression
10. Rules for designing reactors for various types ofreactions